外观模式
外观模式是一种结构型设计模式, 能为程序库、 框架或其他复杂类提供一个简单的接口。
问题
当你在程序种需要使用大量的第三方库以及框架,你会需要管理众多对象,而可能你实际需要使用的能力远没有这么多。众多不重要的对象会增加库的复杂程度,使理解和维护程序很难进行。
解决方案
使用外观模式,外观类对外提供需要的简单接口,简化对复杂子系统的调用。外观将客户端代码的调用转化为对子系统的调用,同时如果客户端没有对子系统的生命周期进行管理,外观需要对此进行管理;子系统如果发生升级和接口变动,只需要修改对应外观类而不需要修改客户端;如果外观变得臃肿时需要将其中部分代码单独抽取为一个新的专用的外观。
优点:
缺点:
模式结构图
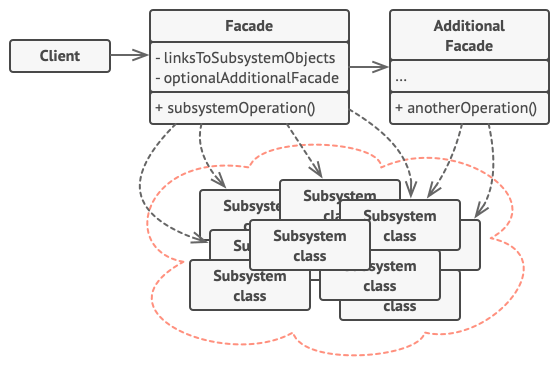
实例
完整代码地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| public class DrawShapeFacade {
public static final int COLOR_GREEN = 1;
public static final int COLOR_RED = 2;
public static final int SHAPE_CIRCLE = 1;
public static final int SHAPE_SQUARE = 2;
public void drawShape(int color, int shape) {
DrawAPI drawAPI = null;
Pen pen = null;
if (shape == SHAPE_CIRCLE) {
drawAPI = new GreenCircle();
} else if (shape == SHAPE_SQUARE) {
drawAPI = new GreenSquare();
} else {
drawAPI = new GreenCircle();
}
if (color == COLOR_RED) {
} else if (color == COLOR_GREEN) {
pen = new GreenPen(drawAPI);
}
if (pen != null) {
pen.draw();
} else {
System.out.println("have not " + color + " pen to draw");
}
}
}
|
适用场景
- 子系统相对复杂且需要的功能相对没那么复杂时可以使用外观模式
- 子系统组织为多层结构可以使用外观模式,为各层次的子系统定制各自的外观,子系统之间只允许通过外观进行交互,降低了子系统之间的耦合
